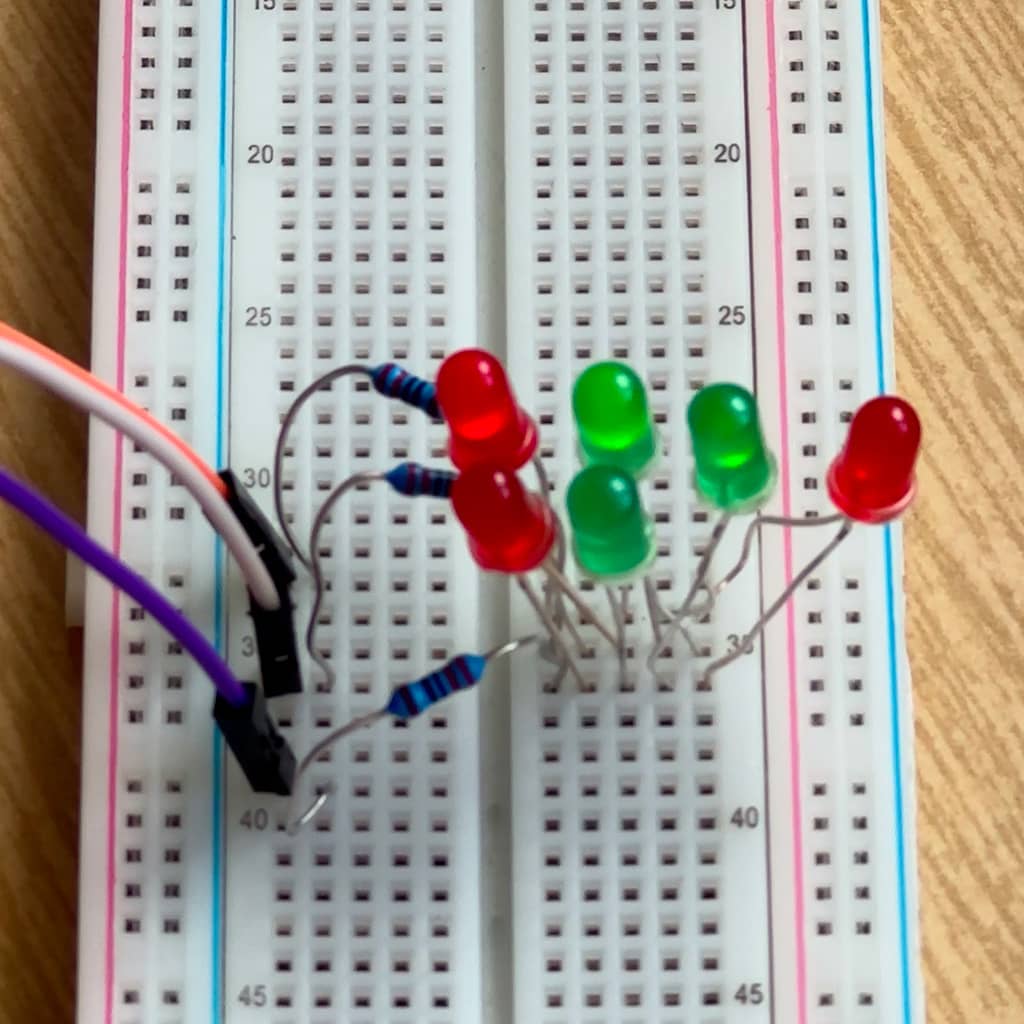
Questa tecnica permette di controllare più LED con un numero limitato di PIN del microcontrollore (un Arduino UNO R4 nel nostro caso) sfruttando il fatto che i LED sono dei diodi che se polarizzati inversamente non si accendono (ma non si rompono se non si supera la tensione di breakdown).
#include "FspTimer.h"
FspTimer audio_timer;
uint64_t count=0;
uint64_t start_time=0;
unsigned long previousMillis = 0;
const long interval = 100;
int c = 0;
#define X1 4
#define X2 3
#define X3 2
const byte LED_pins[6][2] = {
{X1, X2}, {X2, X3}, {X2, X1}, {X3, X2}, {X1, X3}, {X3, X1}
};
bool LED_states[6] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
const byte LED_states_game[10][6] = {
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
void update_LED_states() {
for (byte i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
if (LED_states[i] == 1) {
pinMode(LED_pins[i][0], OUTPUT); //put the LED Anode to OUTPUT
pinMode(LED_pins[i][1], OUTPUT); //put the LED Cathode to OUTPUT
digitalWrite(LED_pins[i][0], HIGH); //put the LED Anode to HIGH
digitalWrite(LED_pins[i][1], LOW); //put the LED Chatode to LOW
delayMicroseconds(350);
pinMode(LED_pins[i][0], INPUT); //put the LED Anode to INPUT
pinMode(LED_pins[i][1], INPUT); //put the LED Cathode to INPUT
}
}
}
void updateLED() {
for (int i=0; i<6; ++i) {
LED_states[i] = LED_states_game[c][i];
}
++c;
if (c >= 10) c=0;
}
// callback method used by timer
void timer_callback(timer_callback_args_t __attribute((unused)) *p_args) {
update_LED_states();
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
previousMillis = currentMillis;
updateLED();
}
}
bool beginTimer(float rate) {
uint8_t timer_type = GPT_TIMER;
int8_t tindex = FspTimer::get_available_timer(timer_type);
if (tindex < 0){
tindex = FspTimer::get_available_timer(timer_type, true);
}
if (tindex < 0){
return false;
}
FspTimer::force_use_of_pwm_reserved_timer();
if(!audio_timer.begin(TIMER_MODE_PERIODIC, timer_type, tindex, rate, 0.0f, timer_callback)){
return false;
}
if (!audio_timer.setup_overflow_irq()){
return false;
}
if (!audio_timer.open()){
return false;
}
if (!audio_timer.start()){
return false;
}
return true;
}
void setup() {
beginTimer(8000);
}
void loop() {
}


Lascia un commento
Devi essere connesso per inviare un commento.